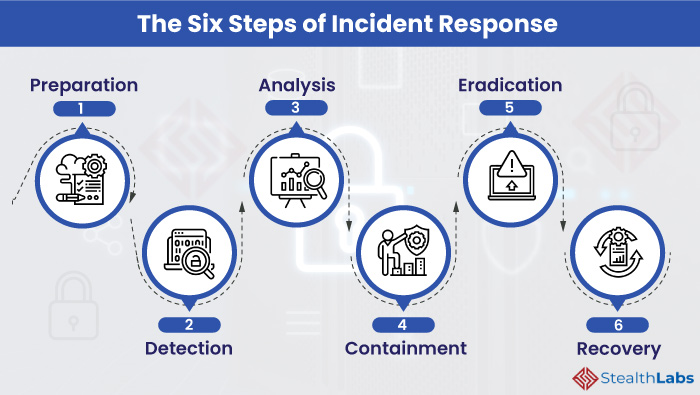
The six steps to build an effective cyber incident response plan
The Six Steps to Build an Effective Cyber Incident Response Plan
Step 1: Prepare and Plan
Cybersecurity incidents have become increasingly common in today's digital age. Without proper planning and preparation, organizations can suffer severe consequences. To build an effective cyber incident response plan, the first step is to prepare and plan.
During this stage, you need to assess potential risks and vulnerabilities, identify critical assets, and prioritize your response efforts. It's crucial to involve all relevant stakeholders, including IT professionals, legal experts, and senior management, to ensure comprehensive planning.
Step 2: Detect and Analyze

Once you have a solid plan in place, the next step is to focus on early detection and analysis. Timely identification of cyber incidents is crucial to minimize the impact and prevent further damage. Establishing an incident detection system and implementing robust monitoring tools can significantly enhance your organization's ability to detect and analyze potential threats.
By continuously monitoring your network and analyzing suspicious activities, you can identify potential security breaches and respond swiftly. This step involves investigating the incident, collecting evidence, and assessing the scope and severity of the attack.
Step 3: Contain and Eradicate

After detecting and analyzing the cyber incident, it's crucial to contain the damage and eradicate the threat. This involves isolating affected systems or networks, disconnecting compromised devices from the network, and taking immediate steps to halt the attack.
Additionally, you need to ensure that all vulnerabilities and entry points exploited by the attacker are identified and patched. This may involve updating software, implementing security patches, and strengthening access controls.
Step 4: Recover and Restore

Once the threat has been contained and eradicated, the focus shifts to the recovery and restoration of affected systems and data. This step involves restoring backups, repairing or replacing compromised hardware, and ensuring that systems are secure and fully operational before reconnecting them to the network.
It's crucial to test restored systems to validate their integrity and ensure they are not compromised. This step also involves communicating with relevant stakeholders, such as customers and employees, to provide updates on the situation and address any concerns they may have.
Step 5: Assess and Learn

After successfully containing the incident and restoring normal operations, it's essential to assess the incident's impact and learn from the experience. Conduct a thorough post-incident analysis to understand the root cause, evaluate the effectiveness of your response plan and procedures, and identify areas for improvement.
By identifying lessons learned, you can implement measures to prevent similar incidents in the future, strengthening your organization's overall security posture. This step also involves updating your incident response plan based on the insights gained from the incident.
Step 6: Review and Test

The final step in building an effective cyber incident response plan is to regularly review and test it. The threat landscape is continuously evolving, and new risks emerge regularly. Therefore, it's crucial to ensure that your response plan is up to date, relevant, and effective.
Conduct regular table-top exercises and simulations to test your plan's efficiency and identify any gaps or weaknesses. Additionally, stay abreast of the latest cybersecurity trends and updates to proactively adapt and enhance your incident response capabilities.
In conclusion, an effective cyber incident response plan is essential for organizations to mitigate risks and protect their sensitive data. By following these six steps - Prepare and Plan, Detect and Analyze, Contain and Eradicate, Recover and Restore, Assess and Learn, and Review and Test - organizations can be better prepared to respond swiftly and effectively to cyber threats. Remember, the key to success lies in proactive planning, continuous monitoring, and regular evaluation.