Respuesta a incidentes de ciberseguridad: guía de nist
Today, we are going to delve into the world of cybersecurity incident response and explore the best practices recommended by experts in the field. Incident response plays a crucial role in protecting organizations from cyber threats and minimizing the impact when incidents occur. Let's start by understanding the incident response lifecycle, depicted in the image below:
Understanding the Incident Response Lifecycle
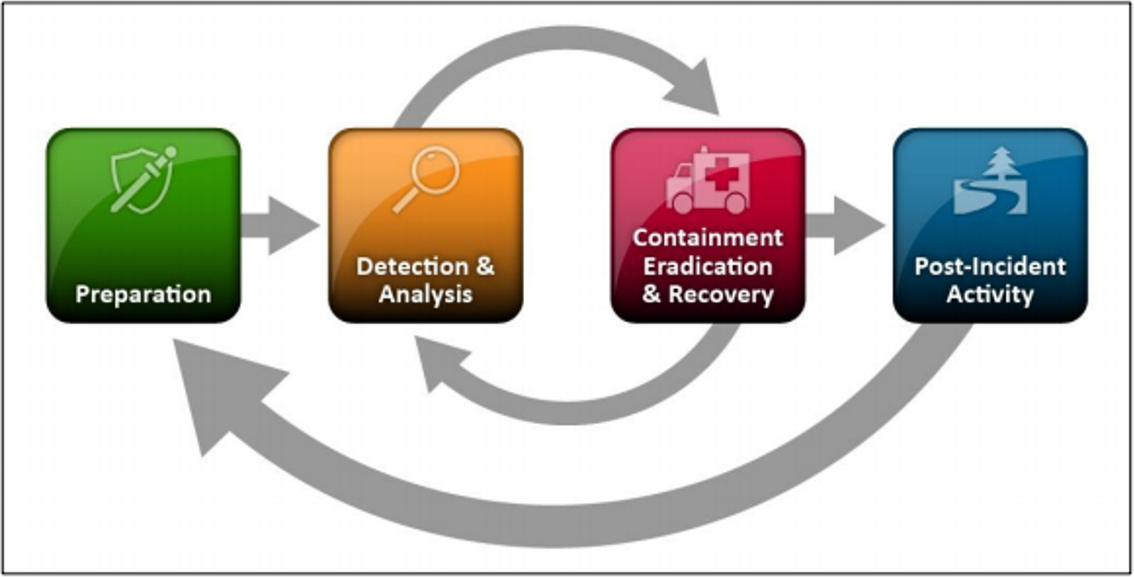
The incident response lifecycle, as illustrated by the National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST), provides organizations with a structured approach to handling cyber incidents. It consists of six key phases: preparation, detection and analysis, containment, eradication and recovery, post-incident activity, and lessons learned.
Preparation involves establishing an incident response team, defining roles and responsibilities, and developing incident response plans and policies. It is crucial to be proactive in identifying potential threats and developing strategies to mitigate them.
Next, in the detection and analysis phase, organizations monitor their networks for any signs of suspicious activity. Intrusion detection systems, log analysis, and threat intelligence platforms play a significant role in identifying threats early.
An Effective Incident Response Plan Template
An essential aspect of incident response is having a well-defined plan in place. The Payment Card Industry Data Security Standard (PCI DSS) provides a useful incident response plan template, as shown above. This template outlines the necessary steps to be taken during different phases of an incident.
Once an incident is detected, the containment phase comes into play. The goal is to prevent further damage by isolating affected systems or devices to limit the attacker's reach. Collecting evidence and maintaining a clear chain of custody are critical during this phase.
The eradication and recovery phase involves removing the identified threat and restoring the affected systems to their normal operation. This may include patching vulnerabilities, cleaning infected systems, and implementing additional security measures.
After the incident has been resolved, it is essential to conduct post-incident activities. This includes analyzing the incident, documenting lessons learned, and identifying areas for improvement in the incident response process.
In conclusion, a well-structured incident response plan is a crucial component of any organization's cybersecurity strategy. By following the incident response lifecycle and utilizing effective incident response plan templates, organizations can effectively respond to cyber incidents and minimize their impact. Remember, being prepared and proactive is key in the ever-evolving landscape of cybersecurity.